The Signs & Symptoms of Gout
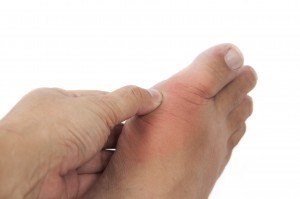 Gout is an arthritic condition which is well known for attacking the metatarsal-phalangeal joint located in the big toe. Studies have shown that nearly half of all diagnosed cases of gout have been located in the patient’s big toe, a type of gout that is known as podagra. While gout often affects the patient’s big toe, this medical condition can also produce arthritic symptoms in the fingers, wrists, knees, and the heels.
Gout is an arthritic condition which is well known for attacking the metatarsal-phalangeal joint located in the big toe. Studies have shown that nearly half of all diagnosed cases of gout have been located in the patient’s big toe, a type of gout that is known as podagra. While gout often affects the patient’s big toe, this medical condition can also produce arthritic symptoms in the fingers, wrists, knees, and the heels.
(Are you looking to enroll in a clinical trial? Please see our list of gout clinical trials.)
In more severe cases of gout, symptoms can include redness, recurring pain, swelling, and tenderness in one or more affected joints. On the other hand, acute cases of gout usually affect just a single joint (mostly the big toe), but the pain it causes can be quite excruciating. The symptoms of gout often get worse at night regardless if it is chronic or acute. However, the worst pain is usually within the first 12 to 24 hours after a gout flare-up.
Common Indications of Gout
The following list of symptoms could indicate a case of gout:
- Joint swelling
- Pain in the joint
- Tenderness around the joint
- Redness in the affected area
- Joints feel hot to the touch
- Experiencing a crushing feeling in the joints
- Elevated pain at night
- Fatigue (more common in men and alcohol drinkers)
- Fever (also more common in men and alcohol drinkers)
- Hyperuricemia
- Urate nephropathy (a rapidly declining kidney function)
- Tophi (deposits of monosodium urate crystals; these are located under the skin)
- Erosion of the bone (caused by tophi)
- Chills
- General feeling of malaise
- Difficulty walking
- Kidney stones (produced from crystallized uric acid and dietary byproducts located in the urine)
There are also a number of other medical conditions which can increase a person’s risk of experiencing an attack of gout:
- Being overweight or obese
- Overeating
- Sickle cell anemia
- Leukemia
- Prior injuries
- Recent trauma
- Dehydration
- Renal disease
- Surgery
- Alcoholism
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Hyperlipidemia
- Diabetes
- Other metabolic syndromes
- Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup
- Hyperuricemia
- Certain medications
The following factors can play a role in the development of Hyperuricemia (high level of uric acid in the bloodstream):
- Overall dietary habits
- Overeating
- Weight gain
- Overproduction of uric acid
- Kidneys are unable to adequately excrete uric acid
- Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup
- Certain medications
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with an attack of gout, please set up an appointment with your doctor right away. When gout is not properly treated it can lead to debilitating pain, permanent joint damage, and bone erosion. Your doctor will be able to develop a treatment plan that is most appropriate for your specific case of gout. While are a number of medications and therapies which can be used to treat your symptoms, not all gout medications are recommended. Once you get your gout symptoms back under control, you can get back to living the life that you want to live.